Welcome to our comprehensive guide to agricultural risk management on the farm! As a farmer, you face a multitude of risks on a daily basis that can impact your operations and bottom line. From unpredictable weather patterns to market fluctuations, it’s essential to have a solid risk management plan in place to protect your livelihood. In this guide, we will explore various strategies and tools that can help you mitigate risks and ensure the long-term success of your farm.
Understanding Agricultural Risk
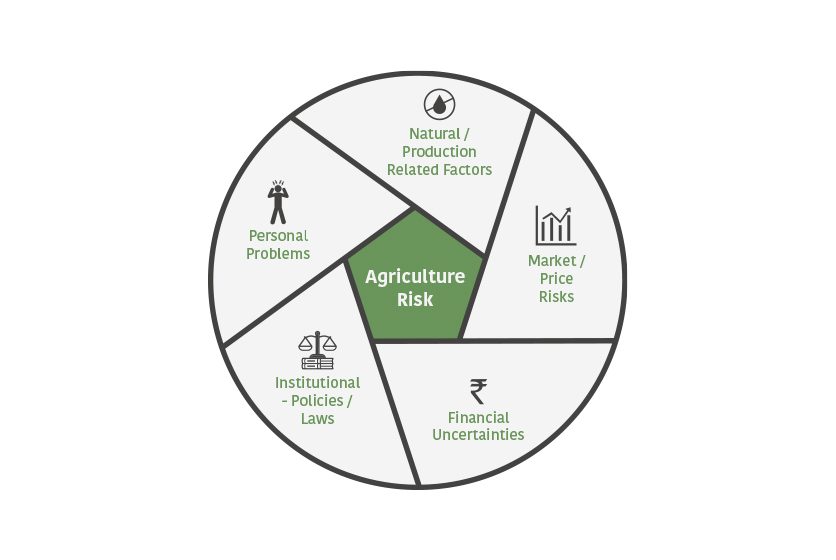
When it comes to agriculture, one of the biggest challenges farmers face is managing risk. Agricultural risk refers to the uncertainties and potential losses that can occur in farming operations. These risks can range from natural disasters such as droughts, floods, or pest outbreaks to market fluctuations, government policies, and even personal health issues. Understanding these risks is crucial for farmers to make informed decisions and develop effective risk management strategies.
One key aspect of understanding agricultural risk is recognizing that it is inherent in the nature of farming. Farmers are at the mercy of unpredictable weather patterns, disease outbreaks, and changing market conditions. This means that no matter how experienced or skilled a farmer may be, there will always be a level of uncertainty and risk involved in agricultural production. Accepting this reality is the first step towards effective risk management.
Another important aspect of understanding agricultural risk is identifying the different types of risks that farmers may face. These can be categorized into four main types: production risk, price risk, financial risk, and institutional risk. Production risk refers to the uncertainties related to crop yields and quality, such as weather conditions, pest infestations, and disease outbreaks. Price risk, on the other hand, relates to the volatility of commodity prices in the market. Financial risk involves issues such as debt management, cash flow fluctuations, and access to credit. Lastly, institutional risk refers to uncertainties stemming from government policies, regulations, and market structures.
It is also essential for farmers to assess the likelihood and potential impact of these risks on their farming operations. This involves conducting a risk assessment by analyzing past data, trends, and current conditions to identify potential vulnerabilities and opportunities for improvement. By understanding the specific risks that they face, farmers can develop tailored risk management strategies to mitigate losses and maximize profits.
Furthermore, understanding agricultural risk also requires farmers to stay informed and up-to-date on industry trends, market developments, and technological advancements. By keeping abreast of changes in the agricultural sector, farmers can anticipate potential risks and take proactive measures to adapt to changing conditions. This may involve investing in new equipment, adopting sustainable practices, or diversifying their crop portfolio to reduce exposure to specific risks.
In conclusion, understanding agricultural risk is a fundamental aspect of successful farming. By acknowledging the inherent uncertainties and complexities of agriculture, farmers can develop proactive risk management strategies to safeguard their operations and ensure long-term sustainability. By identifying and assessing the different types of risks, staying informed on industry developments, and taking action to mitigate potential losses, farmers can navigate the volatile nature of farming and thrive in a challenging environment.
Impact of Climate Change on Farming
Climate change poses a significant threat to the agricultural sector, impacting farming practices and food production worldwide. The unpredictability of weather patterns, such as increased frequency of extreme weather events like droughts, floods, and heatwaves, can have detrimental effects on crops and livestock. These changes in climate conditions create challenges for farmers in managing their operations and adapting to the evolving environment.
One of the most pressing issues caused by climate change is shifting growing seasons. Warmer temperatures and changing rainfall patterns can disrupt traditional planting and harvesting schedules, leading to decreased yields and lower crop quality. Farmers may need to adjust their strategies and invest in new technologies to cope with these changes effectively.
Furthermore, the rise in temperatures can also create challenges for livestock farming. Heat stress can impact animal health and productivity, requiring farmers to invest in cooling systems and provide adequate shelter and water resources for their animals. In addition, changes in precipitation patterns can affect pasture availability and feed quality, further complicating the management of livestock operations.
Another consequence of climate change on farming is an increase in pests and diseases. Warmer temperatures and changing humidity levels create favorable conditions for the proliferation of insects and pathogens that harm crops and livestock. Farmers may need to implement pest control measures and disease management strategies to protect their assets and ensure sustainable production.
Climate change also poses risks to water availability for agriculture. Changes in precipitation patterns and increased evaporation rates can lead to water scarcity in certain regions, impacting irrigation systems and overall crop yields. Farmers may need to adopt water-efficient practices, such as drip irrigation and rainwater harvesting, to mitigate the effects of water scarcity on their operations.
In response to these challenges, farmers and policymakers are increasingly focusing on implementing agricultural risk management strategies. These include diversifying crops and livestock species, investing in climate-resilient technologies, and adopting sustainable agricultural practices. By promoting resilience and adaptability in farming systems, stakeholders can better prepare for the impacts of climate change and ensure food security for future generations.
In conclusion, the impact of climate change on farming is a complex and multifaceted issue that requires proactive solutions and collaborative efforts from all stakeholders. By recognizing the challenges posed by changing climate conditions and implementing effective risk management strategies, the agricultural sector can adapt to the evolving environment and continue to meet the growing demand for food worldwide.
Tools and Strategies for Risk Management
When it comes to managing risks in agriculture, there are various tools and strategies that farmers can utilize to protect their businesses from potential losses. One of the most common tools used for risk management is insurance. Agricultural insurance can provide coverage for a wide range of risks, including crop failures, natural disasters, and market fluctuations. By purchasing insurance policies, farmers can transfer the financial risk of these events to an insurance company, giving them peace of mind knowing that they will be compensated in the event of a loss.
Another important tool for risk management in agriculture is diversification. Diversification involves spreading out the risk by growing different types of crops or raising multiple types of livestock. By diversifying their operations, farmers can reduce their exposure to any single risk factor. For example, if a farmer has both corn and soybean crops, a drought that affects one crop may not have as severe of an impact on their overall income.
In addition to insurance and diversification, farmers can also use futures and options contracts to manage risk. Futures contracts allow farmers to lock in a price for their crops before they are harvested, protecting them from potential price fluctuations in the future. Options contracts give farmers the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a commodity at a specified price at a future date. By using these financial tools, farmers can protect themselves against market volatility and ensure a more stable income.
It is also important for farmers to stay informed about the latest developments in agricultural risk management. By keeping up-to-date with market trends, weather forecasts, and government policies, farmers can make more informed decisions about their operations. This can help them anticipate and mitigate potential risks before they become major problems.
In conclusion, managing risks in agriculture is essential for the success and sustainability of farming operations. By utilizing tools such as insurance, diversification, futures and options contracts, and staying informed about market trends, farmers can protect their businesses from unforeseen events and ensure a more stable income. It is important for farmers to carefully assess their risks and develop a comprehensive risk management plan that takes into account the specific challenges they face in their operations.
Insurance Options for Farmers
When it comes to managing agricultural risks, insurance is a key tool that farmers can use to protect themselves against unforeseen events that could potentially devastate their operations. There are several insurance options that farmers can choose from to help mitigate the risks they face. Here are some common insurance options for farmers:
1. Crop Insurance: Crop insurance is designed to protect farmers against the loss of crops due to natural disasters, such as drought, flood, or hail. This type of insurance can help farmers recover some of the costs associated with replanting crops or making up for lost income. Crop insurance can be especially important for farmers who rely heavily on their crops for income.
2. Livestock Insurance: Livestock insurance provides coverage for farmers against the loss of their animals due to events such as disease, accidents, or theft. This type of insurance can help farmers recoup some of the financial losses they may incur if they lose valuable livestock. Livestock insurance can be crucial for farmers who raise animals for meat or dairy production.
3. Farm Property Insurance: Farm property insurance covers the physical structures and assets on a farm, such as barns, silos, equipment, and machinery. This type of insurance can protect farmers against the costs of repairing or replacing property damaged by events like fire, storms, or vandalism. Farm property insurance is essential for farmers who want to safeguard their investments in their farming operations.
4. Liability Insurance: Liability insurance is another important insurance option for farmers, as it helps protect them from legal claims and lawsuits related to accidents or injuries that occur on their property. For example, if a visitor to the farm is injured by slipping on a wet floor, liability insurance can help cover the costs of medical expenses or legal fees that may arise from the incident. Liability insurance can provide farmers with peace of mind knowing that they are protected in case of unexpected events.
Overall, insurance is a crucial tool for farmers to manage risks and protect their livelihoods. By choosing the right insurance options for their specific needs, farmers can ensure that they are financially secure in the face of unforeseen events that could threaten their operations. It is important for farmers to carefully consider their insurance options and work with a trusted insurance provider to create a comprehensive risk management plan that meets their needs.
Importance of Diversification in Agriculture
When it comes to managing risks in agriculture, diversification plays a crucial role. Diversification refers to the practice of growing a variety of crops or raising different types of livestock on a farm. By diversifying their operations, farmers can reduce their exposure to various risks and uncertainties that can affect their yields and income.
One of the main reasons why diversification is important in agriculture is that it helps farmers spread their risk. For example, if a farmer relies solely on growing a single crop and that crop fails due to adverse weather conditions or pests, they could lose their entire income for the year. However, if the farmer has diversified their operations and grows multiple crops, the impact of a crop failure is less severe. This can help ensure a more stable income for the farmer even in the face of unexpected events.
Diversification also helps farmers take advantage of different market opportunities. By growing a variety of crops or raising different types of livestock, farmers can tap into different markets and have more flexibility in selling their products. This can help reduce their dependence on a single market and increase their chances of finding profitable outlets for their products.
Moreover, diversification can also have environmental benefits. Growing a variety of crops can help improve soil health and reduce the need for chemical inputs, leading to a more sustainable farming system. Diversification can also help promote biodiversity on farms, which is important for supporting ecosystem services and maintaining healthy agroecosystems.
Another key benefit of diversification in agriculture is that it can help improve the resilience of farming systems. By diversifying their operations, farmers can better withstand shocks and stresses, such as extreme weather events or market fluctuations. This can help ensure the long-term viability of their farms and reduce the likelihood of financial losses.
Overall, diversification in agriculture is a key strategy for managing risks and uncertainties in farming. By spreading their risk, exploring different market opportunities, promoting environmental sustainability, and enhancing resilience, farmers can build more robust and sustainable farming systems that can withstand the challenges of a rapidly changing world.
Originally posted 2025-01-13 05:46:17.